
Automatic Blow Molding Machine Troubleshooting Guide for Common Issues
Automatic Blow Molding Machine Troubleshooting Guide for Common Issues
This comprehensive troubleshooting guide from Leshan, an established blow molding machine manufacturer, addresses the most frequent problems encountered with automatic blow molding machines. It covers in detail the core components of these machines, such as the extruder, mold, clamping unit, blow pin, cooling system, and PLC automation, highlighting their roles in producing high-quality plastic bottles and containers. The guide outlines common issues like poor parison formation, incomplete or deformed bottles, excessive flash or burrs, inconsistent bottle weight, and mold sticking or ejection problems. For each issue, it provides clear symptoms, root causes, and step-by-step solutions. Maintenance best practices—such as preventive maintenance routines, proper spare parts management, and operator training—are emphasized to prevent and quickly address machine faults. Advanced troubleshooting techniques, including PLC diagnostics, thermal imaging, and IoT integration, are recommended for resolving complex automation and thermal issues. The guide features real-world case studies showing how Leshan's technical support has solved critical manufacturing problems, along with expert tips for optimizing machine performance. A summary table offers a quick reference for diagnosing and solving common blow molding machine issues. Leshan encourages operators to follow these guidelines and seek technical support for persistent or advanced troubleshooting needs, ensuring efficient, reliable, and high-quality production operations.
As a prominent blow molding machine manufacturer, Leshan has decades of expertise assisting clients to maximize production efficiency and minimize machine downtime. Automatic blow molding machines are crucial for manufacturing high-quality plastic containers, bottles, and parts. However, even the most sophisticated machines can encounter operational issues. This guide aims to provide detailed troubleshooting steps for the most common problems faced in automatic blow molding operations, ensuring smooth and reliable performance.

Understanding Automatic Blow Molding Machines
Automatic blow molding machines are engineered to transform thermoplastic materials into hollow objects such as bottles and containers. These machines automate the entire process, from melting and extruding plastic to forming and cooling the final product. Leshan's portfolio includes extrusion blow molding, injection blow molding, and stretch blow molding machines, each tailored for specific production requirements.
Core Components and Their Functions
- Extruder: Melts and extrudes plastic material into a parison or preform.
- Mold: Shapes the molten or softened plastic into the desired product.
- Clamping Unit: Secures the mold during the forming process.
- Blow Pin: Introduces air to inflate the plastic into the mold cavity.
- Cooling System: Solidifies the product for removal from the mold.
- PLC Controls: Automates and synchronizes machine operations.
Understanding the function of each component is vital for effective troubleshooting.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Steps
Automatic blow molding machines, despite their reliability, can exhibit various issues that affect product quality and machine operation. Leshan recommends systematic troubleshooting, starting with identifying symptoms, isolating causes, and applying proven solutions.
Issue 1: Poor Parison Formation
Symptoms
- Irregular parison thickness
- Parison sticking to the die
- Cold or overheated parison
Root Causes
- Incorrect extruder temperature settings
- Worn or contaminated die head
- Material formulation inconsistency
Troubleshooting Steps
- Check and calibrate extruder temperature zones according to Leshan's recommended specifications.
- Inspect die head for wear or contamination and clean or replace if needed.
- Ensure resin properties match machine requirements; avoid mixing different grades without proper testing.
Consistent parison formation is critical for product quality, so regular monitoring and preventive maintenance are essential.
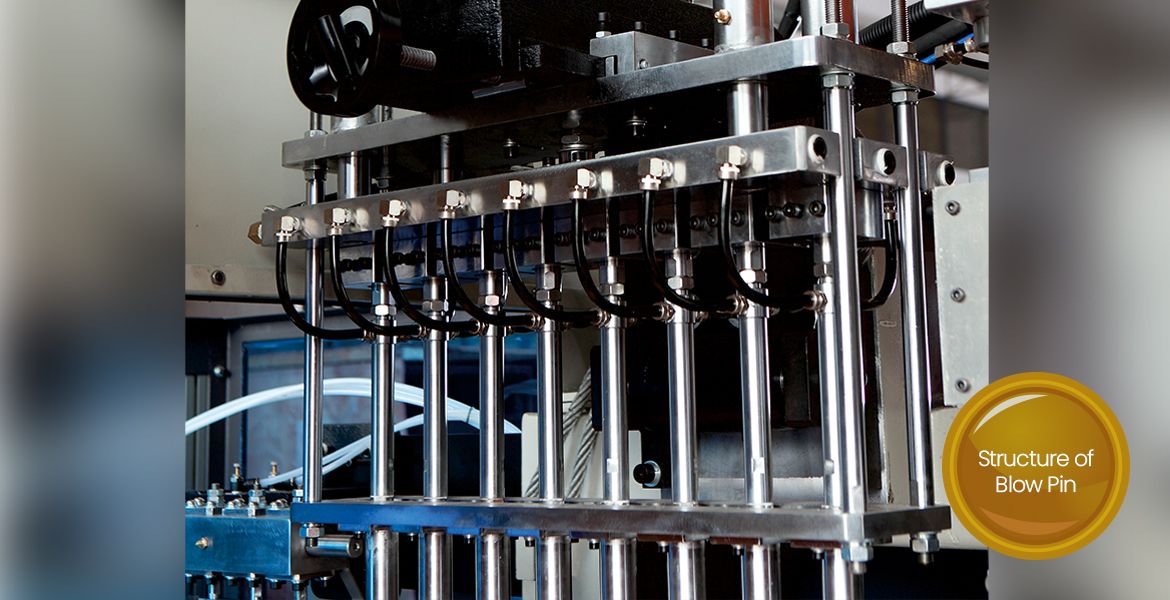
Issue 2: Incomplete or Deformed Bottles
Symptoms
- Bottles with uneven walls
- Collapsed or misshapen containers
- Visible air pockets or bubbles
Root Causes
- Incorrect blowing pressure or timing
- Poor mold alignment or damage
- Insufficient cooling cycle
Troubleshooting Steps
- Set blow pressure and timing according to Leshan's machine control panel reference charts.
- Inspect molds for alignment, wear, or mechanical damage; realign or replace as necessary.
- Extend cooling cycle if product appears soft or deformed; verify cooling system efficiency.
Regular training for operators on machine settings and mold handling can prevent many bottle formation issues.
Issue 3: Excessive Flash or Burrs
Symptoms
- Plastic excess along the bottle seams
- Difficulty in demolding
- Sharp edges on finished products
Root Causes
- Too much clamping force
- Worn mold edges
- Overfilled parison
Troubleshooting Steps
- Adjust clamping force according to Leshan's guidelines for material and product type.
- Inspect and re-machine or replace mold edges if worn.
- Calibrate parison length and extrusion rate to prevent overfilling.
Implementing scheduled mold inspections and calibrations can significantly reduce flash-related problems.
Issue 4: Inconsistent Bottle Weight
Symptoms
- Bottles of varying mass, even within the same batch
- Quality control failures
Root Causes
- Fluctuations in extruder feed rate
- Material temperature inconsistencies
- PLC control synchronization errors
Troubleshooting Steps
- Inspect and calibrate the extruder feed system; ensure uniform pellet supply.
- Monitor and stabilize temperature controls for all heating zones.
- Update or reset PLC program settings, checking for timing mismatches.
Automated weight sensing systems, available in some Leshan models, can help to minimize weight variation.
Issue 5: Mold Sticking and Ejection Challenges
Symptoms
- Products not releasing from the mold
- Surface defects due to forced ejection
Root Causes
- Insufficient mold release agent
- Improper cooling cycle or temperature
- Mold surface damage or contamination
Troubleshooting Steps
- Apply appropriate mold release agents as recommended by Leshan.
- Adjust cooling time and temperature for optimal product solidification.
- Clean or polish mold surfaces to remove contaminants and repair damage.
Frequent cleaning and scheduled maintenance of molds are vital for preventing sticking and improving product finish.
Maintenance Best Practices for Leshan Automatic Blow Molding Machines
Routine Preventive Maintenance
- Daily Checks: Inspect moving parts, lubrication levels, and monitor temperature zones.
- Weekly Tasks: Clean die heads and molds, check for leaks, and verify sensor operation.
- Monthly Inspections: Test PLC programming, calibrate pressure and temperature controls, verify alignment of mechanical components.
Scheduled preventive maintenance reduces the risk of unexpected breakdowns and extends machine lifespan.
Spare Parts Management
- Maintain an inventory of critical spare parts such as heating elements, PLC modules, mold sets, and air valves.
- Use only genuine Leshan parts for replacements to ensure compatibility and performance.
- Train staff to recognize early signs of part wear and initiate replacement proactively.
Proper parts management ensures quick turnaround during repairs and maintenance.
Operator Training and Troubleshooting Skills
- Regularly update operators on Leshan's latest troubleshooting procedures.
- Use visual aids and hands-on practice to enhance understanding of machine functions and faults.
- Document and communicate common issues and successful resolutions for future reference.
Investing in operator training improves machine utilization and minimizes error rates.
Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
PLC and Automation Diagnostics
- Access diagnostic screens to monitor real-time machine parameters.
- Review error logs for patterns and recurring issues.
- Perform software updates and recalibrations as per Leshan's technical bulletins.
Advanced troubleshooting enables quick resolution of complex automation faults.
Thermal Imaging and Monitoring
- Use thermal cameras to detect irregular heating zones and cooling inefficiencies.
- Compare thermal profiles to Leshan's reference standards for optimal operation.
Thermal imaging helps pinpoint invisible problems that may affect product quality.
Remote Support and IoT Integration
- Utilize Leshan's remote diagnostic support for immediate expert assistance.
- Integrate IoT sensors for predictive maintenance and performance tracking.
Leveraging connectivity tools reduces downtime and increases transparency in production.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I prevent contamination in my blow molding process?
- Follow Leshan's recommended cleaning schedules for machines, molds, and material feed systems.
- Use high-quality materials and avoid mixing batches without thorough inspection.
What should I do if my machine frequently stops mid-cycle?
- Check for PLC control errors and reset as needed.
- Inspect sensors and actuators for faults or misalignment.
How often should molds be replaced or serviced?
- Perform visual inspections with every batch change.
- Schedule professional mold servicing every 6-12 months, depending on production volume.
Leshan's customer support is available for detailed guidance and service scheduling.
Case Studies: Leshan Solutions in Action
Case Study 1: Reducing Bottle Weight Variations
A beverage manufacturer experienced inconsistent bottle weights resulting in frequent quality control failures. Leshan's technical team diagnosed temperature fluctuations in the extruder and irregular feed rates. By recalibrating heating zones, replacing worn feed screws, and synchronizing PLC controls, the manufacturer restored stability and achieved uniform bottle weights across batches.
Case Study 2: Eliminating Flash Defects
A packaging facility reported excessive flash formation along the seams of their bottles. Leshan engineers identified over-clamping and worn mold edges as the causes. After adjusting the clamping force and replacing mold edges, flash occurrence was eliminated, reducing rework and improving overall efficiency.
Case Study 3: Minimizing Mold Sticking
An industrial client faced frequent mold sticking and product ejection issues. Leshan recommended applying a specialized mold release agent and extending the cooling cycle. Mold surfaces were also cleaned and polished. The result was a significant reduction in sticking incidents and smoother production flow.
Expert Tips for Optimizing Leshan Blow Molding Machines
- Adhere strictly to Leshan's operation manuals and recommended parameter settings for each product type.
- Establish a cross-functional troubleshooting team to address complex or recurrent issues.
- Implement real-time production monitoring and data analysis for continuous improvement.
- Schedule regular training updates as new machine models and features are introduced.
Combining machine expertise with rigorous process control leads to higher productivity and product quality.
Summary Table: Troubleshooting Common Blow Molding Machine Issues
| Issue | Symptoms | Root Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Poor Parison Formation | Irregular thickness, sticking, cold or overheated parison | Temperature, die contamination, material inconsistency | Calibrate temperature, clean/replace die, check material |
| Incomplete/Deformed Bottles | Uneven walls, collapsed shapes, air bubbles | Blow pressure/timing, mold alignment, cooling | Adjust blow settings, align/repair mold, extend cooling |
| Excessive Flash/Burrs | Seam excess, sharp edges, demolding issues | Clamping force, mold wear, parison overfill | Reduce force, repair mold, calibrate parison length |
| Inconsistent Bottle Weight | Variable mass, QC failures | Feed rate, temperature, PLC errors | Calibrate feed, stabilize temperature, update PLC |
| Mold Sticking/Ejection Problems | Sticking, surface defects | Mold release, cooling, surface damage | Apply release agent, adjust cooling, clean/polish mold |
Contact Leshan for Technical Support
If troubleshooting steps do not resolve your issue or if you require expert guidance for your specific Leshan blow molding machine model, contact Leshan's support team. Experienced technicians are available for on-site service, remote diagnostics, and training programs tailored to your facility's needs.
As a leading blow molding machine manufacturer, Leshan is committed to helping clients overcome operational challenges and achieve consistent, high-quality production. Use this troubleshooting guide to empower your staff, reduce downtime, and ensure the reliability of your automatic blow molding machines.
Tags:EBM blow molding machine application,automatic blow molding machine application,blow molding machine application
